Introduction
Industrial mobility is rapidly evolving due to technological advancements and the pursuit of efficiency. Businesses are adopting advanced systems to improve material and equipment flow, cut costs, and strengthen their competitive advantage. Fundamental solutions like rigid casters are integrated into high-tech systems, enabling safe and efficient movement of heavy loads. The blend of physical and digital innovations is redefining industrial operations, requiring businesses to adapt strategies for real-time market demands. The adoption of these technologies is not just about upgrades, but also about building resilience, ensuring continuity, and future-proofing operations. Collaboration between engineering, IT, and operations teams is crucial for driving productivity forward. Understanding these technologies helps decision-makers adopt sustainable, scalable growth solutions.
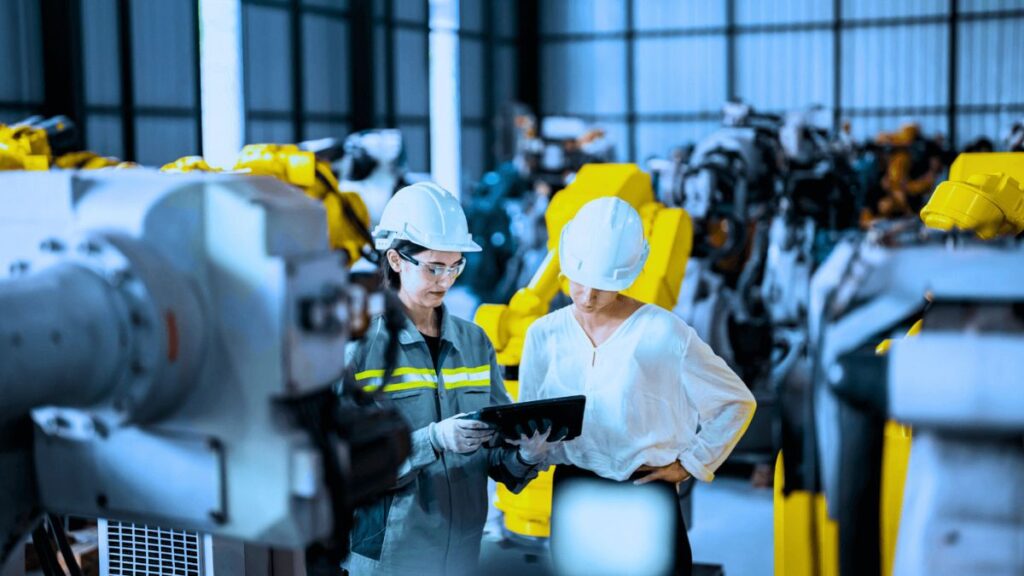
Advanced Robotics in Industrial Settings
Next-generation industrial robotics, equipped with advanced sensors and machine learning, is revolutionizing manufacturing, warehousing, and logistics. Delta robots, known for their speed and dexterity, are used in high-throughput environments like pharmaceuticals and food processing for pick-and-place tasks. Collaborative robots, or cobots, are gaining prominence as they safely share workspace with human operators, handling repetitive or hazardous jobs. This collaboration mitigates safety risks, accelerates workflow, and improves quality control, driving efficiency across various industries.
Autonomous Industrial Vehicles
Industrial mobility solutions rely on intelligent vehicles like Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) to transport goods across facilities and warehouses. AGVs follow fixed routes, ensuring reliable point-to-point transport, leading to cost savings and predictable workflows. AMRs, equipped with advanced navigation and real-time mapping technologies, respond dynamically to changes in environments, making them ideal for distribution centers and e-commerce warehouses. Businesses adopting AMRs report improvements in speed, safety, and labor-related bottlenecks.
Connectivity: Sensors and Networks
Modern industrial environments require real-time awareness and responsiveness, enabled by robust networks and sensors. These sensors gather data on machine health, operational throughput, and environmental conditions, allowing managers to optimize workflows and respond to deviations. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms connect these systems, enabling asset visibility and process automation. Managers can access dashboards, schedule maintenance, and coordinate across supply chain partners. Strong wired and wireless connectivity also facilitates seamless communication between robotics, vehicles, and human operators, enabling fully integrated and automated processes.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing industrial systems by analyzing historical and real-time data, enabling predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and optimized resource allocation. AI-driven predictive analytics forecast component failures, allowing facilities to schedule repairs proactively. AI is also improving route optimization for autonomous vehicles, enhancing manufacturing quality checks, and streamlining supply chain operations. McKinsey & Company reports that integrating AI across industrial workflows can lead to double-digit productivity improvements and innovation opportunities.
Cloud and Edge Computing
The integration of cloud and edge computing is crucial for modern industrial mobility. Edge computing processes data near the source, allowing for immediate responses to operational demands. It is especially important in mission-critical environments where delays can cause ripple effects. Cloud computing offers scalable long-term analysis and secure storage of vast datasets, complementing edge solutions. This layered approach allows organizations to act on data instantly while maintaining strategic decision-making across distributed facilities.
Cybersecurity in Industrial Mobility
Industrial mobility systems are becoming increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats due to increased integration and connectivity. To protect operational integrity and sensitive data, organizations must implement multilayered defense strategies, including regular software patching, network segmentation, robust access controls, and continuous monitoring. Employee training is also crucial, as human error remains a significant risk factor. Proactive engagement from all levels is essential for defending against evolving threats. Innovative solutions combining robotics, autonomous vehicles, smart connectivity, and intelligent analytics are transforming industrial mobility, enabling faster, safer, and more resilient operations.