Introduction
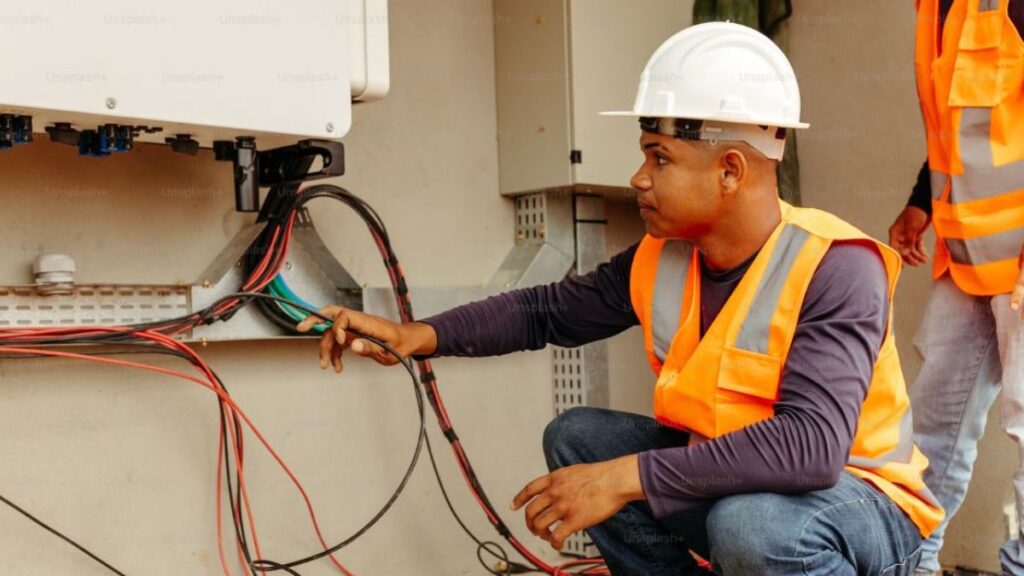
The foundation of modern society relies on energy, and that energy is safely delivered, managed, and used thanks to electrical equipment. These devices not only enable the smooth transmission and utilization of electricity but also form the backbone of everything from residential neighborhoods to large-scale industrial operations. The evolution of these systems reflects ongoing innovation aimed at supporting growing cities, smarter buildings, and more efficient grid networks.
Dependable electrical equipment ensures essential operations across healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and communications sectors. Without it, infrastructure would be vulnerable to power disruptions, inefficiencies, and safety hazards, highlighting why constant development in this field is crucial.
Types of Electrical Equipment
Electrical equipment comprises various components, each performing a specific yet vital function. Understanding these fundamental elements is key to appreciating how power systems keep economies and communities running.
- Transformers: Facilitate voltage adjustment, essential for moving electricity efficiently over long distances while minimizing energy loss during transmission.
- Circuit Breakers: Essential for safety, these automatically interrupt electrical flow in case of overloads or faults, protecting people and property from potential hazards.
- Switchgear: Complex assemblies integrating disconnect switches, fuses, or circuit breakers to manage, control, and isolate portions of the electrical network, ensuring safe operation during maintenance or faults.
- Motors: Convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, powering countless machines in industrial, commercial, and household environments.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
One of the defining features of today’s advanced electrical infrastructure is its focus on energy efficiency. Modern electrical equipment incorporates digital controls, better materials, and advanced design techniques to cut waste and maximize output. The electric motor, a core component in countless applications from industrial machinery to HVAC systems, has seen major improvements in efficiency and performance through variable-speed drives and high-efficiency designs. The move toward smart grids—networks that employ digital technology to monitor and manage power flows—has proven particularly effective at improving transmission efficiency and reducing outages.
Smart monitoring, demand-response technology, and automatic fault detection all play a role in optimizing the use of available resources. For example, as highlighted by a Time article, digitalization in electrical systems can significantly cut carbon emissions and operational costs, leading to environmental and economic benefits.
Integration with Smart Technologies
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed how electrical infrastructure is managed. Today, smart meters and IoT-based sensors offer real-time, granular insights into energy consumption and system health. Facilities managers and utility providers can now pinpoint issues before they escalate, leveraging predictive analytics to schedule maintenance or reroute power during peak loads.
Combining traditional electrical equipment and cutting-edge technology improves system adaptability and resilience. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), digitalization is set to make energy systems more connected, intelligent, efficient, reliable, and sustainable.
Ensuring Safety and Reliability
Protection and reliability are non-negotiable when it comes to electrical systems. Installing devices like Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) and Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) has drastically increased safety, preventing most electrical fires and minimizing the risks of shock or electrocution. These devices detect even subtle deviations in current or voltage and respond instantly to contain hazards.
Advances in monitoring—such as thermal imaging for identifying overheated connections or wireless remote diagnostic systems—enable rapid risk detection. Real-time data ensures that technicians and engineers can act quickly, protecting infrastructure and users from harm.
Supporting Renewable Energy Integration
The global push toward renewables demands electrical equipment capable of handling variable and sometimes intermittent energy sources like solar and wind. Modern systems are designed to integrate these inputs while maintaining grid stability seamlessly. One of the most impactful innovations is grid-scale energy storage—such as advanced battery installations—which store surplus energy generated during periods of high production and release it during periods of peak demand or low generation.
This balancing function is critical as more solar panels and wind farms connect to the grid. Fluctuations could lead to instability or blackouts without robust storage and adaptive grid management. Advanced electrical equipment ensures renewables become a reliable and scalable part of the world’s energy portfolio.
Addressing Cybersecurity Challenges
Cybersecurity poses an urgent challenge in the digital age, with infrastructure systems increasingly interconnected. As more components become smart and remotely accessible, they become more vulnerable to cyberattacks and digital sabotage. Keeping these critical systems secure requires a layered approach—regular software updates, intrusion detection systems, and encrypted communications are now standard practices.
Safeguarding public utilities is crucial for both operational integrity and public safety. Ongoing investment in cybersecurity ensures that the ever-evolving threat landscape does not compromise the electrical systems that societies depend on.
Conclusion
Advanced electrical equipment is essential for the seamless functioning of our homes, industries, and cities. As the world embraces smart technologies, renewable generation, and digital integration, the importance of robust, safe, and efficient electrical infrastructure will only grow. Continuous innovation in this domain is essential—not just for economic progress but also for sustainable, safe, and reliable living in a rapidly changing world.